What Is The Use Of Object Kind Service In Kubernetes
Kubernetes Tutorial

What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is besides known as 'k8s'. This word comes from the Greek language, which ways a pilot or helmsman.
Kubernetes is an extensible, portable, and open-source platform designed past Google in 2014. It is mainly used to automate the deployment, scaling, and operations of the container-based applications across the cluster of nodes. Information technology is also designed for managing the services of containerized apps using different methods which provide the scalability, predictability, and high availability.
Information technology is actually an enhanced version of 'Borg' for managing the long-running processes and batch jobs. Nowadays, many cloud services offer a Kubernetes-based infrastructure on which it can be deployed equally the platform-providing service. This technique or concept works with many container tools, like docker, and follows the client-server architecture.
Key Objects of Kubernetes
Following are the key objects which be in the Kubernetes:
Pod
It is the smallest and simplest basic unit of the Kubernetes awarding. This object indicates the processes which are running in the cluster.
Node
A node is nothing but a single host, which is used to run the virtual or concrete machines. A node in the Kubernetes cluster is also known equally a minion.
Service
A service in a Kubernetes is a logical set up of pods, which works together. With the aid of services, users tin can easily manage load balancing configurations.
ReplicaSet
A ReplicaSet in the Kubernetes is used to identify the particular number of pod replicas are running at a given time. It replaces the replication controller considering it is more powerful and allows a user to use the "set-based" characterization selector.
Namespace
Kubernetes supports various virtual clusters, which are known as namespaces. It is a way of dividing the cluster resource between 2 or more users.
Features of Kubernetes
Following are the essential features of Kubernetes:
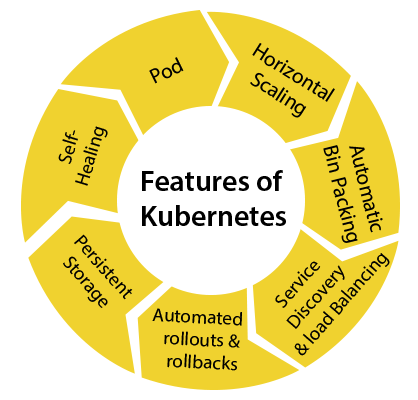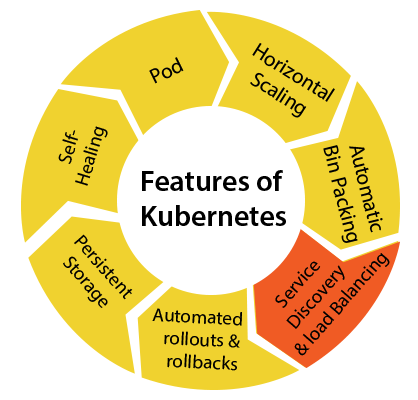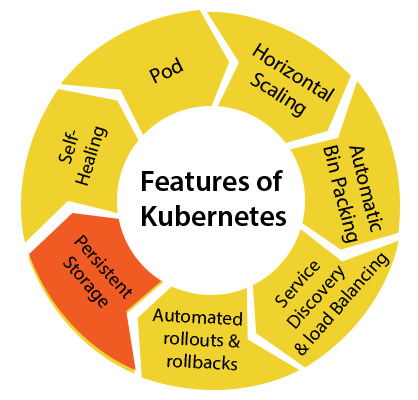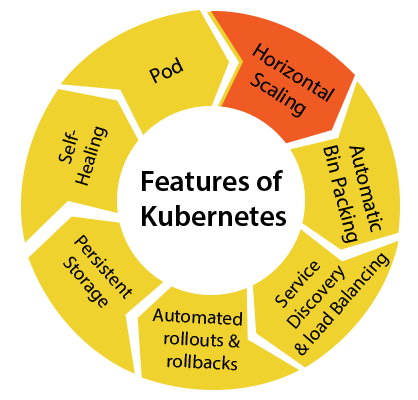
- Pod: It is a deployment unit in Kubernetes with a single Internet protocol accost.
- Horizontal Scaling: Information technology is an important feature in the Kubernetes. This feature uses a HorizontalPodAutoscalar to automatically increase or decrease the number of pods in a deployment, replication controller, replica set, or stateful set on the footing of observed CPU utilization.
- Automatic Bin Packing: Kubernetes helps the user to declare the maximum and minimum resource of computers for their containers.
- Service Discovery and load balancing: Kubernetes assigns the IP addresses and a Proper name of DNS for a set of containers, and also balances the load across them.
- Automated rollouts and rollbacks: Using the rollouts, Kubernetes distributes the changes and updates to an application or its configuration. If whatever problem occurs in the system, then this technique rollbacks those changes for yous immediately.
- Persistent Storage: Kubernetes provides an essential feature called 'persistent storage' for storing the data, which cannot be lost subsequently the pod is killed or rescheduled. Kubernetes supports various storage systems for storing the data, such every bit Google Compute Engine'south Persistent Disks (GCE PD) or Amazon Rubberband Block Storage (EBS). It as well provides the distributed file systems: NFS or GFS.
- Self-Healing: This feature plays an important role in the concept of Kubernetes. Those containers which are failed during the execution process, Kubernetes restarts them automatically. And, those containers which practice not reply to the user-divers health check, information technology stops them from working automatically.
Kubernetes Architecture
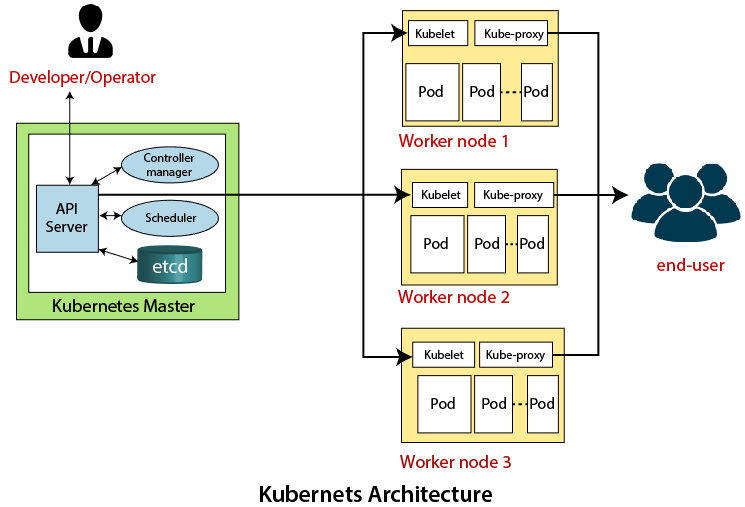
The architecture of Kubernetes actually follows the client-server architecture. It consists of the following ii main components:
- Master Node (Control Plane)
- Slave/worker node
Main Node or Kubernetes Command Plane
The chief node in a Kubernetes architecture is used to manage usa of a cluster. It is actually an entry bespeak for all types of administrative tasks. In the Kubernetes cluster, more than i principal node is nowadays for checking the fault tolerance.
Following are the four different components which exist in the Primary node or Kubernetes Command plane:
- API Server
- Scheduler
- Controller Manager
- ETCD
API Server
The Kubernetes API server receives the Residual commands which are sent by the user. After receiving, it validates the REST requests, process, and then executes them. After the execution of Balance commands, the resulting state of a cluster is saved in 'etcd' as a distributed key-value store.
Scheduler
The scheduler in a master node schedules the tasks to the worker nodes. And, for every worker node, it is used to store the resource usage information.
In other words, information technology is a process that is responsible for assigning pods to the available worker nodes.
Controller Manager
The Controller managing director is too known every bit a controller. Information technology is a daemon that executes in the non-terminating command loops. The controllers in a master node perform a task and manage the state of the cluster. In the Kubernetes, the controller director executes the various types of controllers for handling the nodes, endpoints, etc.
ETCD
It is an open-source, simple, distributed key-value storage which is used to store the cluster data. It is a role of a principal node which is written in a Get programming language.
Now, we accept learned near the performance and components of a chief node; let's see what is the office of a slave/worker node and what are its components.
Worker/Slave node
The Worker node in a Kubernetes is besides known as minions. A worker node is a physical auto that executes the applications using pods. It contains all the essential services which allow a user to assign the resources to the scheduled containers.
Following are the different components which are presents in the Worker or slave node:
Kubelet
This component is an agent service that executes on each worker node in a cluster. It ensures that the pods and their containers are running smoothly. Every kubelet in each worker node communicates with the chief node. It besides starts, stops, and maintains the containers which are organized into pods directly by the chief node.
Kube-proxy
Information technology is a proxy service of Kubernetes, which is executed simply on each worker node in the cluster. The main aim of this component is asking forwarding. Each node interacts with the Kubernetes services through Kube-proxy.
Pods
A pod is a combination of one or more containers which logically execute together on nodes. One worker node can easily execute multiple pods.
Installation of Kubernetes on Linux
The installation of Kubernetes on Linux is a straight forward process. Follow the below steps to install the Kubernetes. In the installation of Kubernetes, each step is mandatory.
Footstep 1: In this stride, we accept to update the necessary dependencies of a system using 2 commands.
The get-go command is used to go all the updates. Execute the following control in the terminal; it will ask to enter the system'due south password.
Output:
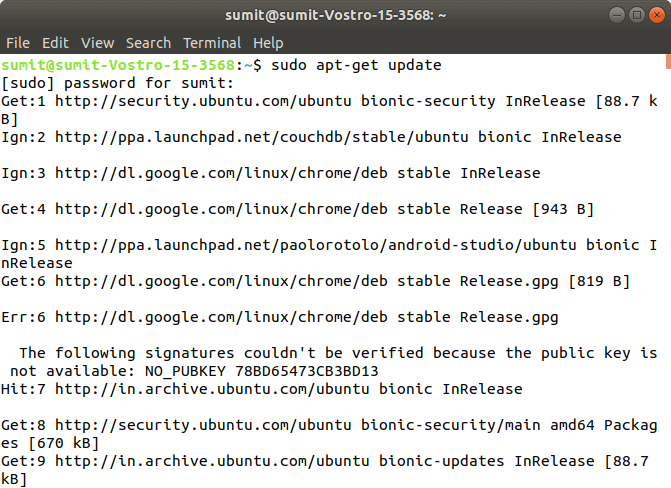
When the beginning command is successfully executed, blazon the following 2d command, which is used to make the repositories.
Output:
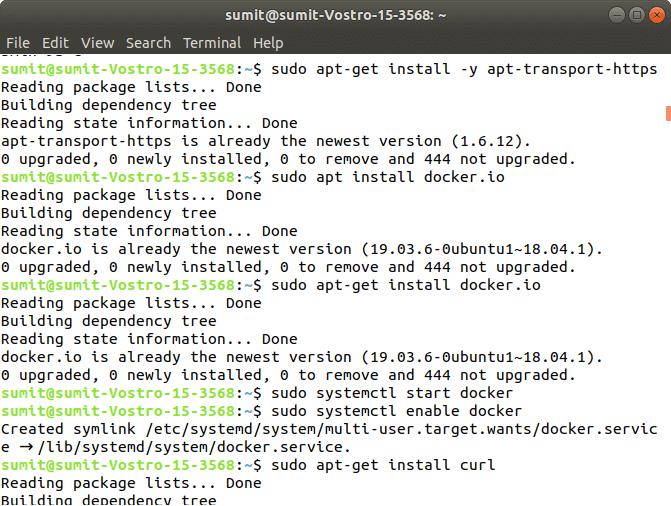
Step 2: Later the above steps are successfully executed, nosotros accept to install the dependencies of docker in this step.
Blazon the following command to install the docker. In the installation process, we have to choose Y for confirmation of the installation.
Output:
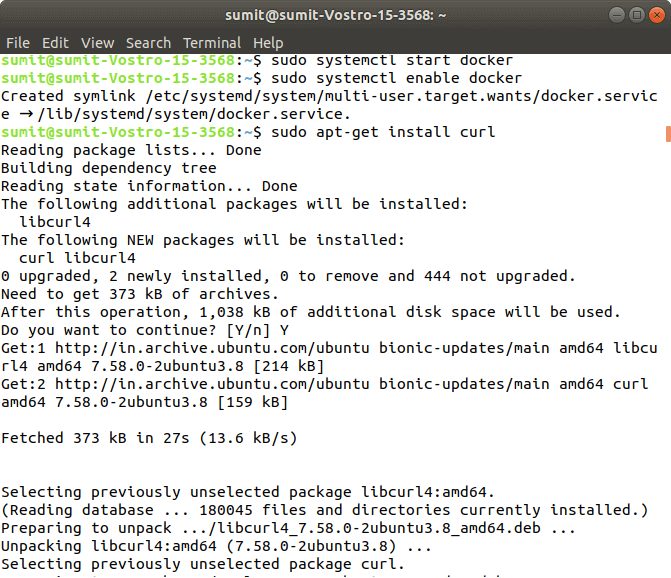
After installing the docker, we take to type the dissimilar two commands for starting and enabling the docker. Type the post-obit first control, which starts the docker:
At present, type the following second command, which enables the docker:
Output:
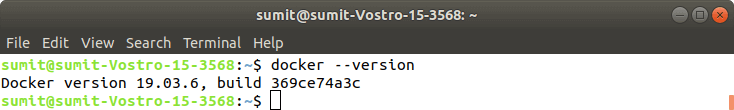
Now, nosotros can check the version of docker by typing the following command:
Output:
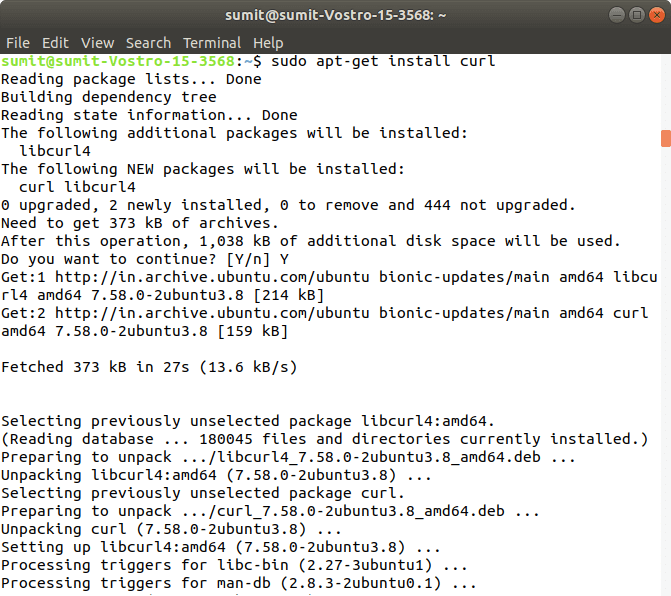
Footstep iii: After the successful execution of all the commands of the 2nd step, nosotros accept to install the scroll command. The roll is used to send the data using URL syntax.
Now, install the curl by using the following control. In the installation, we have to type Y.
Output:
At present, we take to download the add package key for Kubernetes past the following command:
Output:
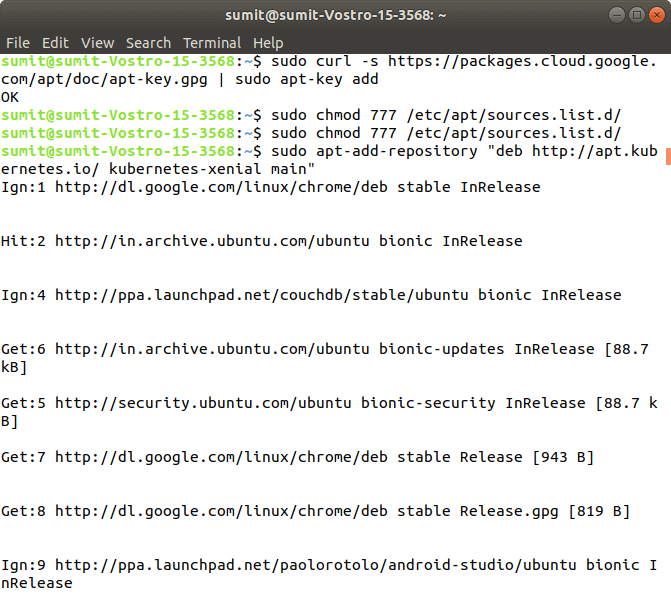
If you get an mistake from the above command, then it means your curl control is not successfully installed, so first install the curl control, and once again run the above control.
At present, we have to add the Kubernetes repositories by the following command:
Output:
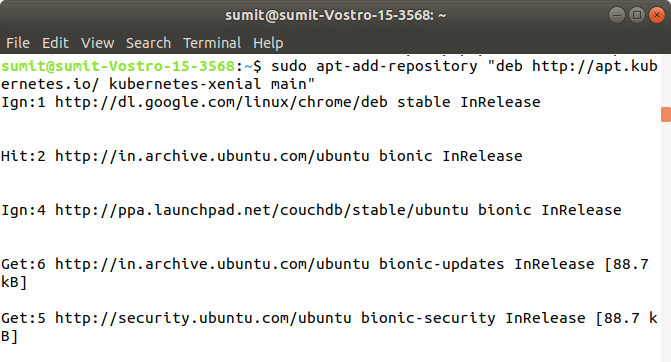
After the successful execution of the above control, we have to check whatever updates by executing the following command:
Output:
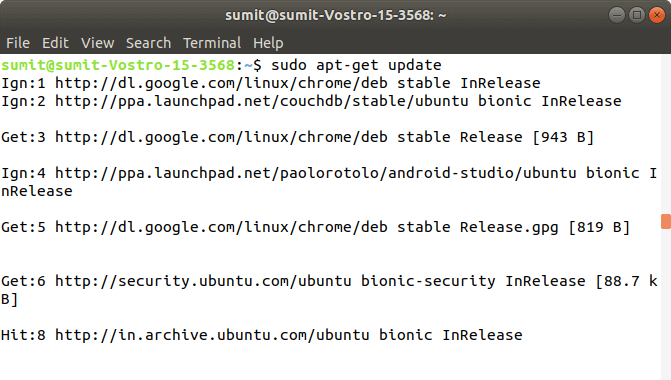
Pace 4: After the execution of the above commands in the to a higher place steps, we have to install the components of Kubernetes by executing the post-obit command:
Output:
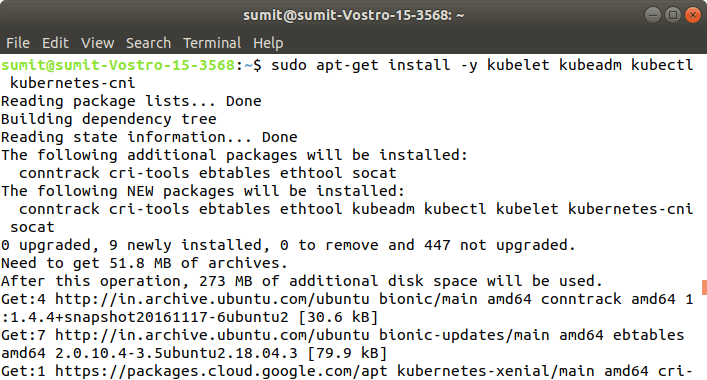
Step 5: After the above installation is done, we have to initialize the kubeadm by executing the following command. The post-obit command disables the swapping on other devices:
Output:
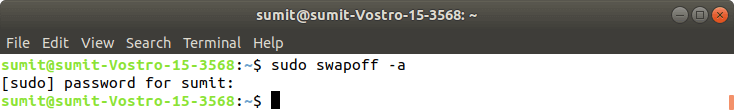
At present, nosotros have to initialize the kubeadm past executing the following command:
Output:
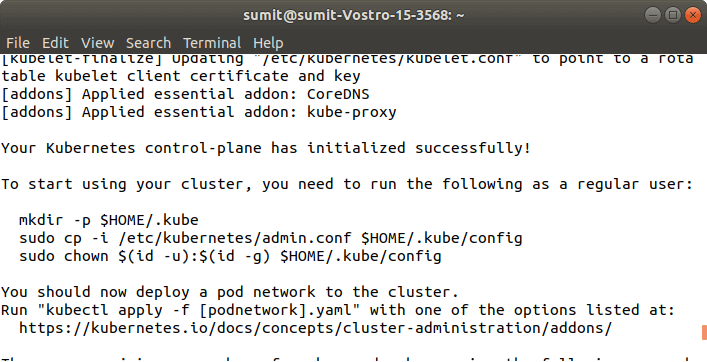
Pace half dozen: Later the above control is successfully executed, we have to run the following commands, which are given in the initialization of kubeadm. These commands are shown in the in a higher place screenshot. The following commands are used to start a cluster:
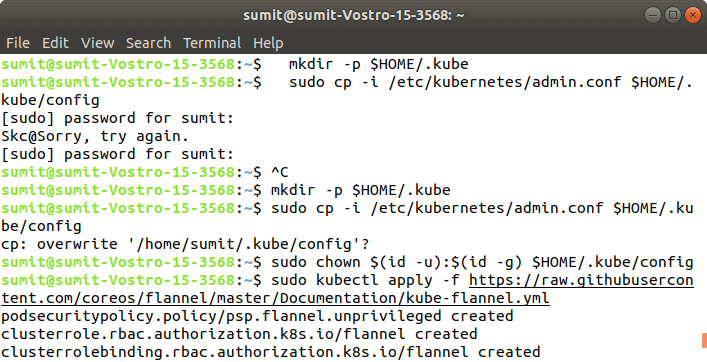
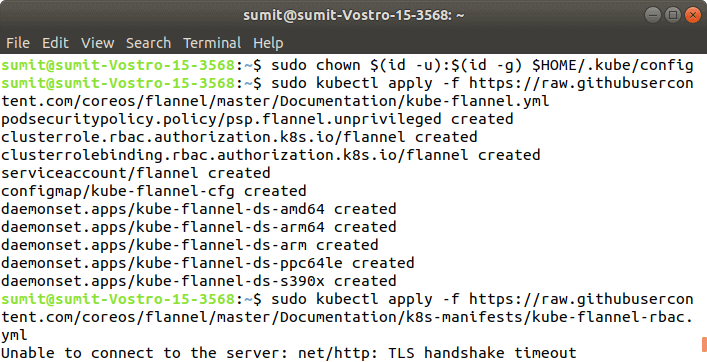
Output:
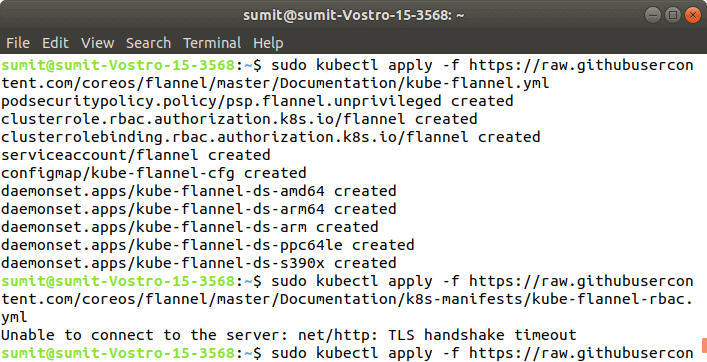
Pace 7: In this step, nosotros have to deploy the paths using the following command:
Output:
Pace 8: Later the execution of the above command, we have to run the following command to verify the installation:
Output:
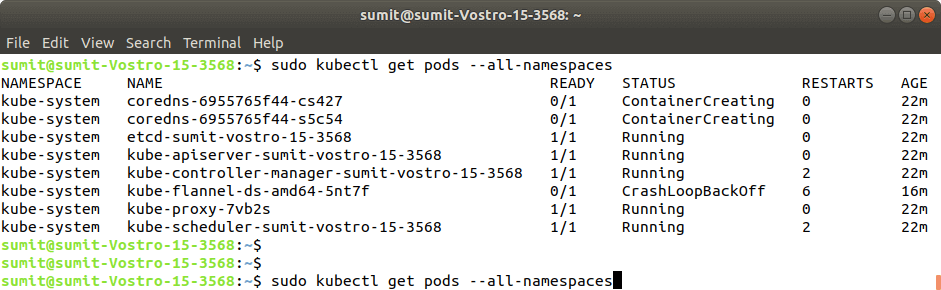
If the output is displayed as shown in the above screenshot. It ways that the Kubernetes is successfully installed on our system.
What Is The Use Of Object Kind Service In Kubernetes,
Source: https://www.javatpoint.com/kubernetes
Posted by: anayadoingunt.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Use Of Object Kind Service In Kubernetes"
Post a Comment